In the world of project management, the Project Management Institute (PMI) asserts that crucial stages pave the way for a successful delivery and contribute to achieving the final objective. In the context of building wind and solar power plants, one such crucial stage is the commissioning of medium-voltage networks, the last step before the plants are energized. Here, developers and contractors face a dilemma: proceed with the necessary caution or succumb to the pressure of time and stakeholders, neglecting this critical phase?
However, giving in to this mistake is not just a risky shortcut but a dangerous gamble. By failing to properly commission medium-voltage networks in renewable energy projects, there is a risk of energizing circuits with undetected irregularities. These irregularities tend to persist after the start of operations and may develop into premature failures—issues that should not occur at this stage.
Beyond the technical and safety aspects, commissioning medium-voltage networks is one of the most important steps in asset optimization. Here, preventive maintenance techniques play a key role in increasing reliability and reducing risks. Additionally, it is advisable to conduct predictive maintenance tests whenever possible. These tests help improve reliability and provide greater security for the next phase of the cables’ operational lifecycle. Below, we explore the recommended techniques for this critical phase in a renewable energy project.
Recommended Tests and Inspections – VLF
| Technique | Suggested reference standards | Justification |
| Applied voltage test on insulation using VLF technology | IEEE 400.2 – 2013 | Main performance test applied to cables before energization to ensure minimum requirements for application. |
| Voltage test applied to the coating | IEC 60229: 2007 | Checking the integrity of the outer sheath to prevent harmful effects of humidity/water. |
| Time domain reflectometry | IEEE 1234 – 2019 | Checking the integrity of metal shields and continuity. Additionally, the speed of light propagation in the cable can be determined for future fault locations, if necessary. |
| Tan delta | IEEE 400.2 – 2024 | Allows the identification of various irregularities and creates a history of the initial reference for predictive monitoring. |
| Partial discharge testing | IEEE 400.3 – 2022 IEC 60270: 2000 | Identification of defects in insulation and accessories. Assessment of the quality of manufactured accessories. IEEE 400.2 – 2013 1EC 60060 |
The applied voltage test for insulation using Very Low Frequency (VLF) technology is, without a doubt, the most important test for identifying weak points and critical defects before energization. Other tests provide numerous benefits, and we strongly recommend conducting them. However, in some cases, they are omitted to reduce immediate financial costs. It is essential to emphasize that reducing the scope of testing increases risks, which may lead to severe short- or long-term consequences.
Recommended Tests and Inspections – Sheath Testing
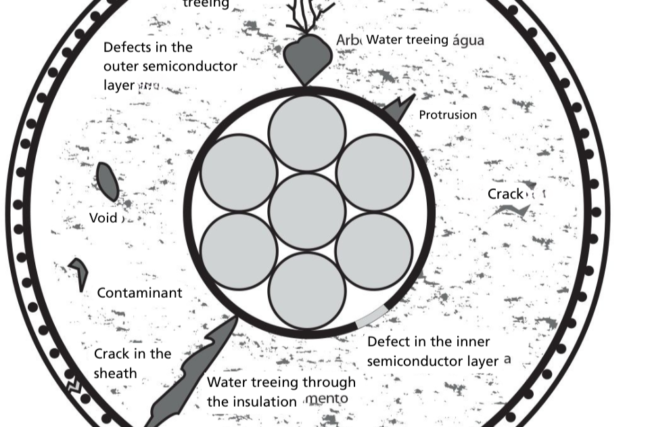
To ensure the absence of failures in cable sheath, preventing and mitigating the effects of moisture and water exposure—and consequently reducing water treeing effects—sheath tests are recommended. It is important to note that these tests should not be performed frequently throughout the cable’s lifecycle. When cables are not mechanically handled or installed in harsh environments, there is no reason to assume defects will develop in the external sheathing. In such cases, performing sheath testing during commissioning and/or occasionally as needed is sufficient.
Recommended Tests and Inspections – Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR)
We strongly recommend its use, as it ensures that metallic shielding remains continuous and in good condition. During installation, excessive mechanical stress may be applied to certain sections of the cable, potentially causing partial shielding rupture. When this occurs, field line distortions and irregular electrical stress in the insulation create weak points that become more susceptible to failure over time.
Other benefits, by analyzing the reflectometry curve and using the precise cable section length (a commonly recorded installation parameter), it is possible to determine the propagation velocity of electrical signals in the cable. This information proves invaluable in future fault events, as it enhances pre-location accuracy and significantly reduces fault location time.
Recommended Tests and Inspections – Tan Delta and Partial Discharge
Applied voltage tests are conducted to ensure that assets meet minimum performance requirements before being put into operation, reducing the likelihood of failures. However, cables that pass the commissioning stage of medium-voltage networks may do so in perfect condition or in less-than-ideal condition. In some cases, a small fraction of cables might fail the test if kept under applied voltage for a few more minutes. Therefore, when possible, it is recommended to perform diagnostic tests to detect latent defects.
Tan delta and partial discharge tests are the most recommended. Tan delta tests will allow the identification of various non-conformities and establish an initial record for predictive monitoring. Meanwhile, partial discharge tests will detect defects in accessories that could fail prematurely after energization.
Finally, in addition to electrical testing, it is essential to highlight the importance of preventive maintenance procedures. During the commissioning phase of the medium-voltage network, it is crucial to inspect the areas, mark the cable routes, prepare the as-built documentation of the installation, and connect the terminations using calibrated torque wrenches.
Related services

VIOLA TD
BAUR viola TD is an device recommended for performing VLF (Very Low Frequency) withstand test and dissipation factor (Tan Delta) test on insulated cables rated up to 20/35 kV.

FRIDA TD
BAUR frida TD is the recommended device for performing VLF (Very Low Frequency) withstand test and dissipation factor (Tan Delta) test on insulated cables rated up to 12/20 kV.

PD-TAD 62
The PD-TaD 62 is a portable Partial Discharge diagnostic system used in conjunction with a VLF source for diagnosing medium-voltage insulated cables.